A screw air compressor is an indispensable piece of equipment in industrial production. Its efficient and stable characteristics make it widely used across various industries, including automotive, electronics, chemicals, metallurgy, and pharmaceuticals. To ensure long-term efficient operation, screw air compressors require regular maintenance. This article provides a comprehensive guide to the key maintenance points for screw air compressors, covering every aspect to help users extend the equipment’s lifespan and reduce the likelihood of failure.
Screw air compressor maintenance involves regular checks of the lubrication, air, cooling, electrical, exhaust systems, and compressor body. Key tasks include changing oil and filters, cleaning air filters and cooling systems, inspecting motors and wiring, and ensuring proper operation of key components. Daily maintenance should focus on cleaning, monitoring performance, and adjusting load. Proper maintenance extends equipment life, improves efficiency, reduces failures, and lowers energy consumption, ensuring a higher return on investment.

1. Key Maintenance Items for Screw Air Compressors
1.1 Lubrication System Maintenance
1.1.1 Lubricant Check and Replacement
- The quality and quantity of the lubricant directly impact the operational efficiency of the screw air compressor. It is essential to regularly check the oil level to ensure it is within the normal range.
- The lubricant typically needs to be replaced every 2,000–3,000 operating hours. Expired or low-quality lubricant will lead to insufficient lubrication, increasing friction and wear.
1.1.2 Replacing the Oil Filter
- Regularly inspect and replace the oil filter to prevent impurities from contaminating the lubricant. It is recommended to clean or replace the oil filter every 500 hours of operation.
1.1.3 Cleaning the Oil Cooler
- The oil cooler may accumulate dirt, causing the oil temperature to rise and impacting lubrication efficiency. The oil cooler should be cleaned and inspected annually.
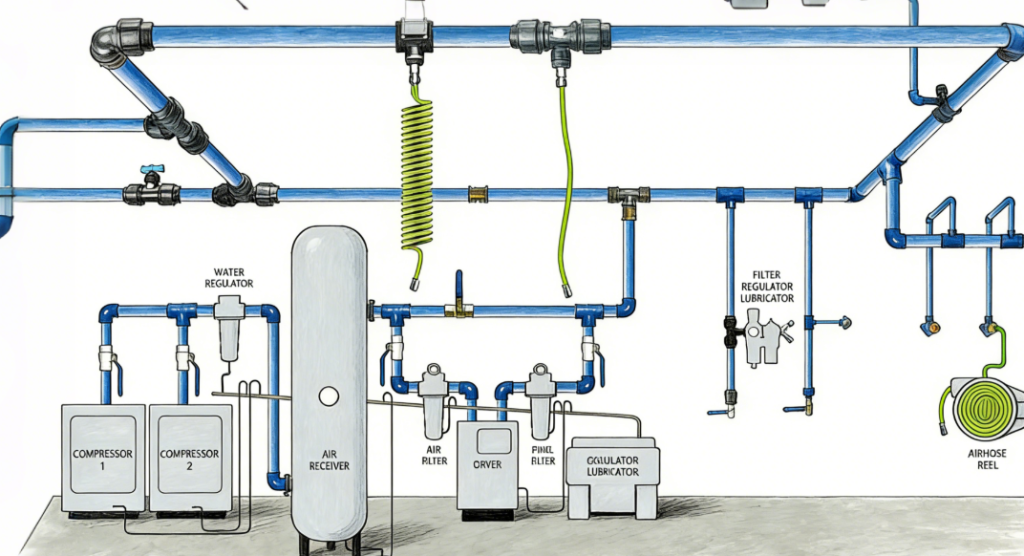
1.2 Air System Inspection and Maintenance
1.2.1 Air Filter Maintenance
- The air filter is a critical component that prevents impurities from entering the compressor. It should be inspected regularly, and cleaned or replaced as necessary. Check the filter every 500–1,000 hours (specific intervals depend on the dust concentration in the working environment).
1.2.2 Compressed Air Drying System
- If the compressor is equipped with a dryer (either refrigerated or desiccant), the desiccant should be regularly checked. The performance of the dryer is crucial for the quality of the compressed air, as outdated desiccant can cause air moisture, which affects downstream equipment.
1.3 Cooling System Inspection and Maintenance
1.3.1 Cleaning the Cooler and Radiator
- The cooling system is vital for maintaining the normal working temperature. The cooler and radiator should be regularly cleaned to prevent dust and oil buildup, which could reduce cooling efficiency. Also, inspect the cooler piping for leaks.
1.3.2 Checking the Cooling Fluid Temperature and Flow
- For water-cooled compressors: Check the flow and temperature of the cooling water to ensure proper cooling performance.
- For air-cooled equipment: Ensure the fans and air intake are unobstructed.
1.4 Electrical System Inspection
1.4.1 Checking the Motor and Electrical Connections
- Inspect the motor insulation, cable aging, and connection terminals for looseness. Any issues found should be promptly repaired or replaced.
1.4.2 Control Panel and Automation System Check
- If an automated control system is used, inspect the control panel and sensors to ensure the equipment responds accurately to operational commands. Check for stability in current and voltage to avoid electrical faults that could lead to downtime.
1.5 Exhaust System and Safety Valve Inspection
1.5.1 Checking the Exhaust Piping
- Periodically inspect the exhaust piping to ensure there are no blockages or leaks. Keep the pipes clean and clear to reduce exhaust pressure.
1.5.2 Inspecting the Exhaust and Safety Valves
- The exhaust and safety valves are essential for preventing overpressure faults. Regularly inspect these valves to ensure they open and close properly and are free from wear or corrosion.
1.6 Screw Compressor Body Inspection
1.6.1 Checking the Screw, Bearings, and Seals
- Regularly inspect the screw for wear, the bearings for lubrication, and the seals for integrity. Overly worn screws and bearings should be replaced promptly to avoid further damage.
1.6.2 Checking for Mechanical Vibration
- The screw air compressor should not experience abnormal vibrations during operation. If excessive vibration occurs, it could indicate improper installation or internal component failure, and the unit should be stopped for inspection.
2. Daily Maintenance and Maintenance Strategies for Screw Air Compressors
2.1 Regular Cleaning and Dust Removal
- Keep the exterior of the equipment and surrounding environment clean. Clean the machine’s exterior daily, removing dust and oil, ensuring that the air filter, cooler, and radiator remain free of dust.
2.2 Monitoring Operational Data and Performance
- Utilize an intelligent monitoring system to continuously track the equipment’s working condition through sensors for temperature, pressure, oil levels, and vibrations. Any data anomalies should be promptly analyzed to prevent potential failures.
2.3 Regularly Checking Consumable Parts
- Inspect and replace consumable components, such as seals and air valves, to prevent minor issues from escalating into major mechanical failures.
2.4 Adjusting Compressor Load and Pressure
- Regularly check the equipment’s operating load and pressure settings to ensure it is not running in an overloaded or low-load state. Using a variable speed drive (VSD) can help automatically adjust the load based on demand, reducing energy consumption.
3. Common Problems and Solutions for Screw Air Compressors (FAQ)
Q1: How should I deal with overheating in a screw air compressor?A1: Overheating is often caused by cooling system malfunctions or insufficient lubricant. First, check whether the cooler and radiator are clean and ensure the cooling system is functioning correctly. Next, check the oil level and quality, and replace the oil if necessary. If the problem persists, check if the exhaust temperature is too high and adjust the compressor load accordingly.
Q2: How do I repair oil leakage in a screw air compressor?A2: Oil leaks are typically caused by worn seals or loose connections. Inspect all oil seals and pipe connections to ensure there are no loose or worn parts. Replace any damaged seals promptly.
Q3: How can I diagnose vibration in a screw air compressor?A3: Vibration may be caused by an imbalanced rotor or worn bearings. First, check the bearing wear and lubrication status to ensure they are operating properly. If the vibration is excessive, stop the compressor and inspect or replace any damaged components.
Q4: What should I do if the screw air compressor has insufficient exhaust?A4: Insufficient exhaust could be due to a clogged air filter, blocked exhaust pipe, or damaged compressor components. First, inspect and clean or replace the air filter. Next, check whether the exhaust pipe is clear. Finally, inspect the compressor’s screws and bearings for wear.
Q5: How can I improve the energy efficiency of my screw air compressor?A5: You can improve energy efficiency by:
- Using a variable speed drive (VSD) to automatically adjust the load according to demand.
- Regularly cleaning the cooling system to prevent poor heat dissipation.
- Selecting the appropriate operating mode to avoid extended low-load operation.
- Checking and repairing any gas leaks to prevent energy waste.
4. Conclusion
By implementing regular maintenance, precise servicing, and timely fault elimination, a screw air compressor can ensure stable operation, reduce failure rates, and increase efficiency. Professional maintenance not only extends the equipment’s lifespan but also improves productivity, lowers energy consumption, and ultimately yields higher return on investment. MINNUO recommends that businesses establish a comprehensive maintenance plan and continuously monitor equipment condition to ensure the compressor remains in optimal working condition over the long term.




 Email
Email sales:+86 15366749631
sales:+86 15366749631

