In the world of air compressors, understanding SCFM (Standard Cubic Feet per Minute) and CFM (Cubic Feet per Minute) is crucial for making informed decisions. These metrics measure the flow rate of compressed air, but they do so under different conditions.
SCFM measures air flow under standardized conditions, ensuring consistency across different environments, while CFM reflects the actual air flow at the specific conditions of operation. To convert SCFM to CFM, consider the current temperature and pressure compared to standard conditions. For accurate equipment performance evaluation, SCFM is preferred as it normalizes variations in ambient conditions.
This article aims to clarify these concepts, provide practical insights, and guide potential buyers through the nuances of SCFM and CFM.
Air Flow Measurement
To effectively evaluate and utilize air compressors, it’s important to grasp the fundamental concepts of air flow measurement. While both SCFM and CFM are used to quantify air flow, they serve different purposes and are measured under different conditions. Understanding these basic terms will provide a solid foundation for comparing and choosing air compressors.
What is CFM (Cubic Feet per Minute)?
CFM measures the volume of air moved by the compressor per minute. It is the raw, unadjusted flow rate and varies with changes in ambient conditions such as temperature and pressure. For example, at higher altitudes where air density is lower, CFM measurements can fluctuate significantly. This measurement is essential for understanding the actual performance of an air compressor under given operational conditions.
What is SCFM (Standard Cubic Feet per Minute)?
SCFM provides a standardized measurement by normalizing air flow to specific standard conditions—typically 68°F (20°C) and 14.7 psi (1 atm). This standardization allows for consistent comparisons between different equipment and operating environments. SCFM is particularly useful when evaluating compressors for diverse applications where conditions vary.
How to Calculate SCFM and CFM
With a clear understanding of CFM and SCFM, the next step is learning how to calculate these metrics accurately. Proper calculation is crucial for comparing different compressors and ensuring that they meet your specific needs. This section will guide you through the formulas and methods required for calculating both CFM and SCFM.
Calculation of CFM
To calculate CFM, measure the volume of air the compressor delivers in cubic feet over one minute. The formula is straightforward:
CFM=Time (in minutes)/Volume (in cubic feet)
This calculation provides a direct measurement of the compressor’s output under current conditions.
Calculation of SCFM
Converting CFM to SCFM involves accounting for standard conditions to normalize the measurement. The conversion formula is:
SCFM=CFM×(Pstd/Pactual)×(Tactual/Tstd)
Where:
- Pstd and Tstd are the standard pressure and temperature
- Pactual and Tactual are the actual pressure and temperature
Converting between SCFM and CFM
Understanding the ambient conditions where the compressor operates allows you to convert SCFM to CFM and vice versa. For example, if a compressor is rated at 100 SCFM at standard conditions but operates at 80°F and 10 psi, the actual CFM will be different. This conversion helps in accurately evaluating performance across different settings.
Key Differences Between SCFM and CFM
Having established how to calculate SCFM and CFM, it’s essential to understand the differences between these measurements. Knowing how they compare will help you make more informed decisions when selecting air compressors for various applications. This section explores the core distinctions and their implications.
The Role of Standard Conditions
SCFM standardizes air flow to ensure consistency in performance evaluations. By normalizing measurements to specific standard conditions, SCFM allows for reliable comparisons between different compressors and environments. This is particularly useful when comparing equipment across different locations and operational settings.
Influence of Ambient Conditions on CFM
CFM can vary greatly with changes in temperature and pressure. For instance, at high altitudes, the lower air density means that CFM readings can be lower than at sea level. This variability highlights why SCFM is often preferred for standardized comparisons, as it normalizes the data and accounts for environmental changes.
Why SCFM is Important
Understanding the significance of SCFM is crucial for evaluating equipment performance and making accurate comparisons. While CFM provides real-time data, SCFM offers a standardized measure that can be crucial for precise performance assessment and operational efficiency.
The Relevance of SCFM in Accurate Performance Evaluation
SCFM is vital for accurate performance assessment, especially in environments where conditions vary. By providing a normalized measure, SCFM ensures that performance metrics are comparable regardless of external factors. This standardization is key for industries requiring consistent air flow rates.
SCFM and Equipment Efficiency
Using SCFM helps in evaluating how efficiently a compressor performs under standardized conditions. This can be particularly useful for industries where consistent performance is critical, such as in manufacturing and pneumatic tools. SCFM provides a clearer picture of equipment efficiency and reliability.
CFM in Practical Applications
While SCFM is important for standardized comparisons, CFM plays a crucial role in day-to-day operations. Understanding how CFM is used in practical applications will help you assess how well a compressor meets specific operational needs.
How CFM is Used in Day-to-Day Operations
CFM is typically used in real-world scenarios where the actual flow rate is measured. This helps in assessing how well the compressor performs in specific operational conditions, such as in a workshop or production facility. Accurate CFM measurements ensure that the compressor meets the demands of its intended application.
Examples of Industries where CFM is Commonly Used
Industries like automotive repair and woodworking often rely on CFM measurements to ensure that compressors meet the demands of their specific applications. Adjusting for actual operating conditions allows for more accurate performance assessments and better equipment selection.
Comparing SCFM and CFM: When to Use Each
With a solid grasp of SCFM and CFM, the next step is to understand when to use each measurement. This knowledge will guide you in selecting the right compressor for your needs, ensuring optimal performance in various settings.
SCFM Provides a More Accurate Representation
SCFM is preferable for technical evaluations and comparisons, especially when compressors are used in varying environmental conditions. It provides a normalized metric that is useful for understanding performance across different settings and ensuring accurate comparisons.
CFM is Sufficient
For practical, day-to-day operations where conditions are relatively stable, CFM measurements are often adequate. They offer a direct understanding of how much air the compressor delivers under current conditions, which is sufficient for many operational assessments.
Guidelines for Choosing Between SCFM and CFM
When deciding between SCFM and CFM, consider the application environment and the specific performance needs. SCFM is ideal for standardized comparisons, while CFM is useful for operational assessments where environmental conditions are stable.
Converting SCFM to CFM: Practical Examples
To further illustrate the practical application of these concepts, let’s explore how to convert SCFM to CFM with specific examples. Understanding these conversions helps in accurately evaluating compressor performance across different conditions.
4 SCFM to CFM
Assuming standard conditions of 68°F and 14.7 psi, and an actual condition of 80°F and 12 psi:
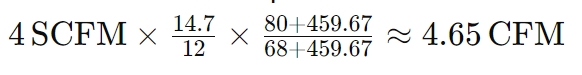
5 SCFM to CFM
Using the same standard conditions, and an actual condition of 90°F and 10 psi:
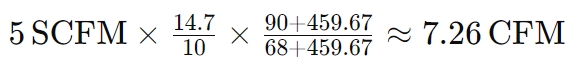
These examples demonstrate how SCFM values can be converted to CFM based on varying operational conditions, providing a clearer understanding of compressor performance.
Practical Considerations for Potential Buyers
When choosing an air compressor, it’s crucial to interpret SCFM and CFM specifications correctly. This section will guide you through practical considerations to ensure you select the right equipment for your needs.
Interpreting SCFM and CFM Specifications
When reviewing air compressor specifications, check whether the ratings are provided in SCFM or CFM. Understanding these terms helps in selecting equipment that matches your operational needs and ensuring accurate performance assessments.
Factors to Consider When Choosing an Air Compressor
Consider factors such as the operating environment, required air flow rate, and specific application needs. Choosing the right metric ensures that the compressor performs efficiently and meets your requirements.
Tips for Ensuring Accurate Measurement and Performance
Regularly calibrate and maintain your equipment to ensure accurate CFM and SCFM readings. Adjust for environmental conditions as needed to maintain performance and reliability.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between SCFM and CFM is essential for evaluating air compressor performance and making informed purchasing decisions. SCFM provides a standardized measure, useful for comparisons, while CFM reflects actual operational conditions. By considering these metrics, you can select the most suitable equipment for your needs and ensure optimal performance. If you have questions on these metrics, you can contact our engineers to give you targeted explanations and recommendations!
Misconceptions about SCFM and CFM
- “SCFM is just another term for CFM”: SCFM accounts for standard conditions, while CFM reflects actual conditions.
- “CFM and SCFM are interchangeable”: They are not; SCFM normalizes data for comparison, whereas CFM shows real-time performance.
Frequently Asked Questions
SCFM stands for Standard Cubic Feet per Minute, a measure of air flow standardized to specific conditions.
SCFM allows for consistent performance comparisons by standardizing measurement conditions.





 Email
Email sales:+86 15366749631
sales:+86 15366749631

