Imagine a world where the simple act of compressing air could power industries, save lives, and even make daily tasks easier. That’s the magic of compressed air—a force so versatile and reliable that it’s become the backbone of many critical operations across the globe. Whether you’re inflating your car tires, powering a manufacturing plant, or operating life-saving medical equipment, compressed air is at work behind the scenes, making everything possible.
So, what is Compressed Air? Compressed air is a form of stored energy created by forcing air into a smaller volume, which increases its pressure. This versatile resource powers a wide range of tools and machinery across various industries, from manufacturing to healthcare, making it essential in modern technology.
In this article, we’ll dive deep into the world of compressed air, exploring what it is, why it’s so essential, and how it drives our modern world forward.
What is Compressed Air?
Compressed air is more than just air squeezed into a smaller space. Compressed air is a powerful form of stored energy that can be harnessed for countless applications. By compressing air to a fraction of its original volume, we significantly increase the pressure, which can then be released to perform work. Humans have used the principles of air compression for thousands of years, but modern technology has truly unlocked its potential.
Basic Principles of Compressed Air
To truly understand the power and potential of compressed air, we must first explore its fundamental principles. These principles form the foundation upon which all compressed air applications are built, ensuring that we can harness this energy source effectively and efficiently.
The principle of compressed air involves mechanically compressing air to a higher pressure, thereby increasing its kinetic and potential energy for use in various industrial and everyday applications.
Steps for compressed air
Air Compression:
- Intake: The air compressor first draws in air from the atmosphere.
- Compression: The air is then compressed by a piston, screw, or turbine, reducing its volume and increasing its pressure. This process forces the air molecules closer together, storing more energy in the form of high-pressure air.
- Storage: The compressed air is typically stored in a pressure tank or reservoir for later use.
Energy Conversion:
- Kinetic Energy Storage: Compressed air holds significant energy due to its high pressure. When released, this energy converts into kinetic energy, which can drive various tools and equipment.
- Applications: Compressed air is used in a wide range of applications, such as powering pneumatic tools, blowing away dust, controlling pneumatic systems, transmitting power, and operating actuators in industrial automation systems.
Pressure Release and Application:
- Pressure Regulation: During use, compressed air is transported through pipelines, where pressure regulators ensure the appropriate pressure is delivered to the application equipment.
- Energy Release: As compressed air is released, it rapidly expands, converting stored energy into mechanical work to perform specific tasks, like powering pneumatic motors or tools.
Characteristics of Compressed Air
Once air is compressed, it takes on several unique characteristics that make it an invaluable tool in various industries. These characteristics include pressure, volume, and moisture content, all of which play crucial roles in how compressed air is used and managed.
Compressed air has distinct characteristics that make it valuable for various applications:
- Pressure: The pressure of compressed air is measured in pounds per square inch (PSI), and it determines the force with which the air is released.
- Volume: The amount of air compressed, usually measured in cubic feet per minute (CFM), affects how much work the air can perform.
- Temperature: Compressing air generates heat, so cooling systems are often necessary to maintain optimal operating conditions.
- Moisture Content: Air naturally contains moisture, which can condense during compression. Moisture control is essential to prevent damage to equipment and ensure the quality of the compressed air.
Applications of Compressed Air
Now that we’ve covered the basics, let’s move on to the real-world applications of compressed air. This energy source is incredibly versatile, making it a staple in numerous industries. Understanding these applications will give you a deeper appreciation of why compressed air is so crucial in today’s world.
Industrial Applications
In manufacturing, compressed air is indispensable. It powers pneumatic tools, drives automation systems, and plays a crucial role in CNC machining. The precision and consistency of compressed air make it ideal for tasks that require accuracy and speed.
Automotive Applications
Compressed air’s role in the automotive industry is equally significant. From tire inflation to operating brake systems, this powerful resource ensures that vehicles are safe, efficient, and aesthetically pleasing. Its ability to deliver consistent pressure is key to these processes.
Medical and Healthcare Uses
In healthcare, the reliability and cleanliness of compressed air are paramount. It powers respiratory equipment, dental tools, and surgical instruments, all of which require precise and safe operation. The clean, dry air provided by medical-grade compressors ensures patient safety and effective treatment.
Other Common Uses
Beyond industrial and medical applications, compressed air finds its way into our homes and small businesses. Whether it’s spray painting, cleaning, or inflating tires, compressed air offers an efficient and accessible solution for many everyday tasks.

Why Do We Use Compressed Air?
With such a wide range of applications, you might wonder what makes compressed air the go-to choice for so many industries. The reasons are rooted in its versatility, efficiency, and reliability, all of which contribute to its widespread adoption and continued use.
Versatility Across Industries
One of the primary reasons we use compressed air is its versatility. It can be adapted to countless tasks, from powering heavy machinery to operating delicate medical instruments. This adaptability makes it a critical component in various industries.
Efficiency and Speed
Compressed air is a powerhouse when it comes to efficiency and speed. In manufacturing, it drives automation systems that increase production rates, while in the automotive industry, it powers tools that make repairs quicker and more accurate.
Reliability and Safety
Compressed air is a reliable and safe energy source. Unlike electricity, it doesn’t spark, making it suitable for environments where flammable materials are present. Its consistent pressure ensures that tools and machinery operate smoothly, reducing the risk of malfunctions.
Environmental and Economic Considerations
In today’s world, environmental and economic factors are more important than ever. Compressed air not only helps in reducing energy consumption but also contributes to cost savings, making it an environmentally friendly and economically viable choice.
Types of Air Compressors
As we’ve seen, the applications of compressed air are vast and varied. But to harness this power, we need the right tools—air compressors. Understanding the different types available will help you choose the best one for your specific needs.
Reciprocating Air Compressors
Reciprocating compressors, also known as piston compressors, are among the most common types. They are favored for their durability and ability to handle intermittent use, making them ideal for smaller operations.
Rotary Screw Air Compressors
For continuous operation in industrial settings, rotary screw compressors are often the go-to choice. Their efficiency and reliability make them popular in environments where large volumes of compressed air are required.
Centrifugal Air Compressors
Centrifugal compressors are designed for high-capacity operations. They use centrifugal force to compress air, making them ideal for large industrial applications where consistent and powerful air output is necessary.
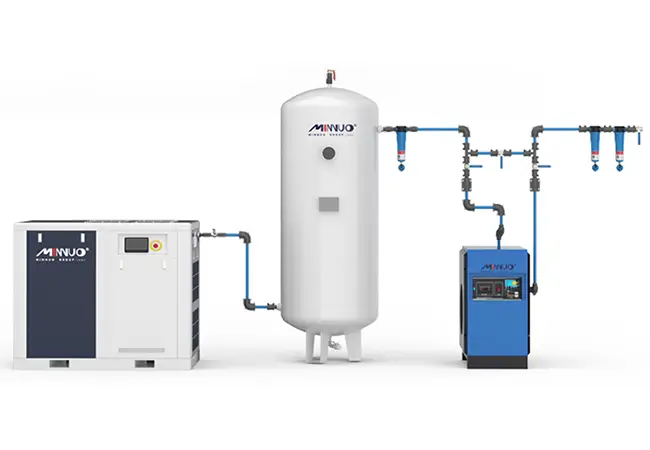
Components of a Compressed Air System
Having the right compressor is just one part of the equation. A well-designed compressed air system comprises several components that work together to ensure efficient and reliable operation. Understanding these components is crucial for anyone looking to optimize their system.
Air Compressor
At the heart of any compressed air system is the compressor itself. Selecting the right type of compressor depends on your specific needs, including the pressure, volume, and quality of air required.
Air Dryer
Air dryers play a vital role in maintaining the quality of compressed air. By removing moisture, they prevent damage to equipment and ensure the air is suitable for its intended use. Choosing the right air dryer is essential for the long-term reliability of your system.
Air Receiver Tank
The air receiver tank is more than just a storage unit; it helps to maintain consistent pressure within the system and reduces the workload on the compressor. This component is critical for ensuring the efficiency and longevity of your compressed air system.
Filters and Regulators
Filters and regulators are key to maintaining air quality and pressure. Can remove contaminants, while regulators control the pressure, ensuring that your compressed air system operates smoothly and effectively.
Distribution System
The distribution system, consisting of piping and hoses, is responsible for delivering compressed air to the point of use. A well-designed distribution system minimizes pressure drops and ensures that air is delivered efficiently and reliably.

Future Trends in Compressed Air Technology
The field of compressed air technology is continually evolving, driven by advancements in engineering and a growing emphasis on sustainability. As industries strive to reduce their environmental impact and improve efficiency, several key trends are shaping the future of compressed air systems.
Advances in Compressor Technology
One of the most significant trends is the development of more energy-efficient compressors. Innovations such as variable speed drives (VSD) allow compressors to adjust their output based on demand, reducing energy waste and operating costs. These advancements are making compressed air systems more adaptable and economical, particularly in large-scale industrial applications.
Integration with IoT and Industry 4.0
The integration of compressed air systems with the Internet of Things (IoT) and Industry 4.0 technologies is another transformative trend. These smart systems enable remote monitoring and predictive maintenance, allowing businesses to optimize performance and reduce downtime. By collecting and analyzing real-time data, companies can make informed decisions that enhance efficiency and extend the lifespan of their equipment.
Sustainable Practices
Sustainability is a driving force behind many of the changes in compressed air technology. As companies seek to reduce their carbon footprint, there is a growing emphasis on using green technologies and practices. This includes the adoption of energy-efficient compressors, the use of renewable energy sources, and efforts to minimize air leaks and other forms of energy waste. The result is a more sustainable approach to compressed air that benefits both the environment and the bottom line.
As technology continues to evolve, so too will the role of compressed air in our lives. Its reliability, efficiency, and environmental benefits make it a cornerstone of modern industry.
FAQs
Compressed air is safer in hazardous environments, as it doesn’t produce sparks. It’s also highly reliable and versatile, making it suitable for a wide range of applications.
Consider the specific requirements of your application, including the pressure and volume of air needed, as well as the operating environment. Consulting with a specialist can also help you choose the best compressor.
Regular maintenance includes inspecting and replacing filters, checking for leaks, servicing the compressor, and ensuring that the system components are functioning correctly.
Yes, advancements in compressor technology and energy-efficient systems are making compressed air an environmentally friendly option, particularly when combined with sustainable practices.
Industries such as manufacturing, automotive, healthcare, and construction benefit significantly from compressed air systems due to their versatility, reliability, and efficiency.




 Email
Email sales:+86 15366749631
sales:+86 15366749631

