Air compressors are essential in industrial production, powering various pneumatic tools across industries like machinery manufacturing, automotive, chemicals, and electronics. However, many companies face challenges like high energy consumption or frequent malfunctions, which can increase operational costs and disrupt production. Calculating the CFM to kW ratio and reassessing compressor specifications can help address these issues effectively.
To calculate the CFM to kW ratio of an air compressor, one must first locate the compressor’s CFM (cubic feet per minute) rating in the manufacturer’s specifications. Then, find the motor’s kW (kilowatt) rating on the compressor’s nameplate. Finally, use the formula “CFM to kW ratio = CFM ÷ kW” to calculate. If automation tools are preferred, a CFM to kW calculator can simplify the selection process and help assess efficiency, aiding in the selection of the appropriate compressor specifications.

Concepts of CFM and kW
CFM
CFM, or cubic feet per minute, is an important indicator for measuring the volume of air an air compressor can deliver in one minute. It plays a critical role in assessing the performance of the compressor, as it directly relates to the operating speed and power output of pneumatic tools.
In addition to CFM, other units of airflow measurement, such as cubic meters per hour (m³/h) or liters per second (L/s), exist. These units may be used in different countries, industries, or specific applications. However, CFM remains the most commonly used and significant metric for air compressors due to its broad application history and industry recognition. It can directly reflect the compressor’s air delivery capacity under specific conditions, providing a key basis for selecting the right equipment.
kW
In the context of industrial air compressors, kW represents the power required to run the compressor’s motor. It is also a crucial factor in determining compressor efficiency and has a direct and significant impact on energy consumption and overall operational costs.
Why Calculate the CFM to kW Ratio?
Improving Compressor Selection Efficiency
Selecting the right compressor is a crucial decision in a company’s production operations. By accurately calculating the CFM to kW ratio, businesses can more precisely determine the appropriate air compressor specifications based on their unique production needs. This means companies can find a compressor that provides adequate power for production processes, ensuring pneumatic tools and equipment operate efficiently without wasting excess energy.
For instance, in an electronics manufacturing company, pneumatic devices on the production line have specific air pressure and flow requirements. By calculating the CFM to kW ratio, businesses can select the most suitable compressor for their production line, avoiding unnecessary costs from selecting equipment with either too much or too little power. Oversized equipment not only incurs higher purchase costs but also wastes energy due to low-load operation. On the other hand, undersized equipment cannot meet production needs, affecting efficiency.
Therefore, calculating the CFM to kW ratio helps businesses make precise compressor selections, improving equipment utilization and return on investment.
Identifying Inefficiencies
Calculating the CFM to kW ratio provides a valuable tool for businesses to identify potential inefficiencies in their current compressor systems. By comparing actual operating data with the ideal CFM to kW ratio range, businesses can detect specific areas of energy waste.
For example, if the calculated ratio is significantly lower than industry standards or the normal level for similar equipment, it may indicate issues such as internal leaks, inefficient motors, or clogged air filters.
Businesses can then address these potential problems through detailed inspections and corrective measures, such as repairing leaks, replacing motors with higher efficiency models, or cleaning air filters. In the long term, these measures can significantly reduce energy consumption, lower operational costs, and improve overall economic performance. Additionally, by continuously monitoring the CFM to kW ratio, businesses can detect trends of declining compressor performance and proactively plan for maintenance and upgrades to ensure stable production.
Increasing Productivity
Optimizing the CFM to kW ratio of air compressors has a positive effect on increasing productivity. When the ratio is within a reasonable range, it ensures that pneumatic tools receive stable, sufficient, and appropriate air pressure and flow. In this optimal working environment, pneumatic tools can operate at their best, completing tasks with higher speed and accuracy.
For example, in a machining workshop, pneumatic cutting tools, when supplied with the right compressed air, can process workpieces faster and more precisely, reducing processing time and scrap rates, thereby increasing output speed and product quality. Furthermore, stable compressed air supply reduces the frequency of production interruptions due to tool failure or instability, ensuring continuous and efficient production processes.
Therefore, by calculating and optimizing the CFM to kW ratio, businesses can create more favorable conditions for the production process, enhance tool efficiency, and improve overall productivity.
How to Calculate the CFM to kW Ratio
The steps to calculate the CFM to kW ratio of an air compressor are relatively simple and include the following key steps:
Find the CFM Rating
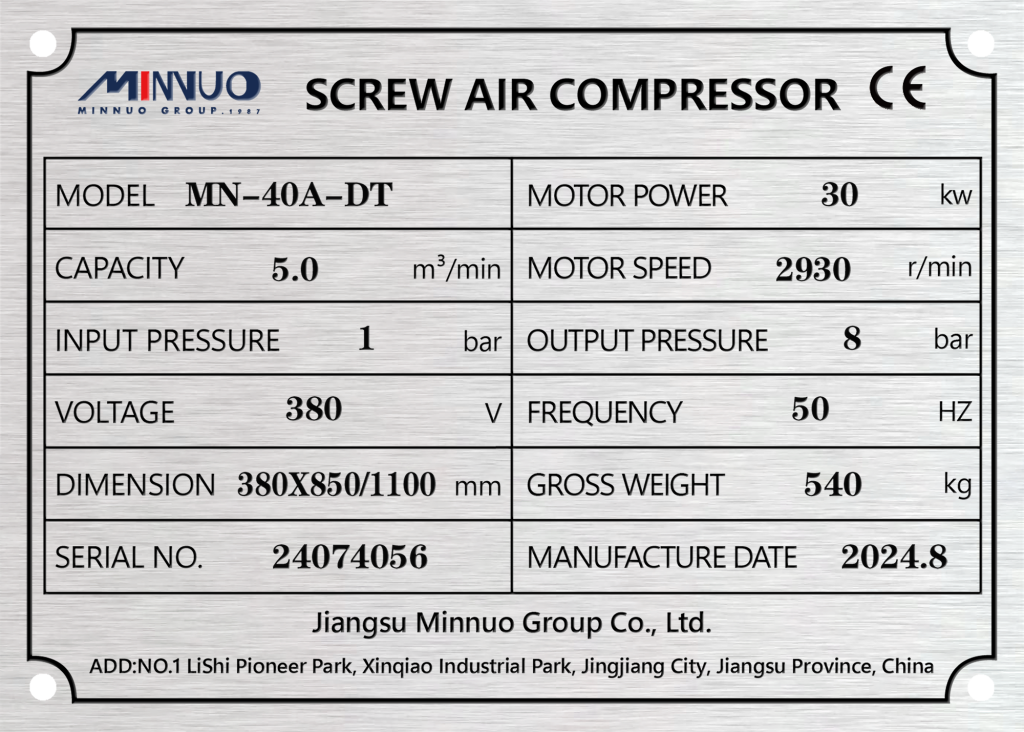
First, businesses need to look up the CFM (cubic feet per minute) rating in the product specifications provided by the compressor manufacturer. This value is usually determined under specific testing conditions and represents the maximum airflow the compressor can output under ideal conditions. For example, if a compressor’s specifications list a CFM rating of 50, it means the compressor can deliver 50 cubic feet of air per minute under standard test conditions.
When looking up the CFM rating, businesses must ensure the specifications match the actual compressor model being used and note the working conditions (such as pressure range and intake temperature), as these factors can influence the actual airflow.
Find the Motor’s kW Rating
Next, businesses need to check the motor’s kW (kilowatt) rating on the compressor’s nameplate. The kW rating reflects the power required to operate the motor. For instance, if the motor’s nameplate indicates a kW rating of 10, it means the motor requires 10 kW of power to drive the compressor. Again, it’s important to ensure the working conditions and standards align with the provided kW rating for accurate data.
Use the CFM to kW Ratio Formula
After obtaining both the CFM and kW ratings, the ratio can be calculated using the formula:
CFM to kW Ratio = CFM ÷ kW
For example, if the CFM rating is 30 and the kW rating is 5, the calculation would be:
30 ÷ 5 = 6, meaning the CFM to kW ratio is 6. This calculation reflects the efficiency relationship between air output and power input.
If businesses prefer to use automated tools, they can utilize a CFM to kW calculator to simplify the selection process. These calculators, based on specific algorithms and databases, can be used for various compressor models and specifications. By entering the appropriate CFM and kW values, the calculator will quickly provide the ratio and efficiency evaluation, making it easier for businesses to select the right compressor.
Reference CFM to kW Ratio Chart
Typically, a fixed air compressor produces 4 to 6 CFM of airflow for every 1 kW of power output. However, this number can vary depending on factors like compressor type, manufacturing process, internal structure, and overall operating efficiency. Below is a sample chart of power output versus CFM output:
| Power Output (kW) | CFM Output |
|---|---|
| 1 kW | 4 – 6 CFM |
| 5 kW | 20 – 30 CFM |
| 10 kW | 40 – 60 CFM |
| 25 kW | 100 – 150 CFM |
| 50 kW | 200 – 300 CFM |
| 100 kW | 400 – 600 CFM |
This chart provides a useful reference for evaluating air compressor efficiency. By comparing the actual compressor’s power output and CFM output with the chart, businesses can gauge whether their compressor’s efficiency is within an acceptable range.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the CFM to kW ratio is crucial for production operations. By understanding and accurately calculating this ratio, businesses can identify compressor inefficiencies, preventing reduced output and increased costs, and ensuring better support for sustainable development and competitiveness.
If you have any further questions, feel free to contact MINNUO!





 Email
Email sales:+86 15366749631
sales:+86 15366749631

